Abstract
The roles of school library have been changing, and thus the roles of school librarians. Based on the various realities in different schools, the author compared roles of libraries and also librarians in reality with these in ideal IB documents.
Key Words: Library, Librarian, School, Ideal Library, Roles, IB
Content
1.1 Rational of the Present Study
1.2 Research Objective of the Thesis
1.3 Research Methodology of the Thesis
1.4 Significance of the Present Study
Chapter Two An Analysis of the Ideal Library and Library in Reality
2.2 Library in the IB Documentation & in Our practices
2.2.2 Take what the Author Did for an Example
2.2.3 What the Author Saw Other Librarians Do?
Chapter Three Theoretical Framework
3.1 How is Library Described in IB
4.1 Main Conclusions and Findings
4.2 Limitations and Implications for Further Study
IB International Baccalaureate
ATL Approaches to learning (IB Education)
1.1 Rational of the Present Study
Most of the schools in all over China have realized that they rely on libraries more and more, but some do not know clearly the roles of the library or the librarians, thus in different school libraries and librarians have different roles most of which might have a very vague distinguishment from the admin people or technology people. But there are good examples of schools which are getting very close to the definition of what an ideal library should be in IB documents.
1.2 Research Objective of the Thesis
By making comparisons, we can realize what reasons result the differences, what support should schools provide for libraries and librarians, and what change should librarians make to their roles to make their working more smoothly and meaningful.
1.3 Research Methodology of the Thesis
The author uses a qualitative researching method. Firstly, the author compares several schools; Secondly, the author uses what she learns through an IB library workshop.
1.4 Significance of the Present Study
The study can give some suggestions and refers to schools and librarians that are struggling in building the roles of their libraries.
Chapter Two An Analysis of the Ideal Library and Library in Reality
The library/ian system can be misunderstood, or practices can evolve around it that do not support or energize learning. Librarians across the IB community were asked about practices that they felt did not promote the library as a system that aids and extends learning and teaching. (“Misinterpreting the role of the library/ian” in Ideal Libraries: a guide for schools)
“There are exciting conversations happening in schools on how to prepare young learners for an increasingly connected and complex world. Information is readily available in most countries, and any person with an internet-ready device can produce content that could potentially become public knowledge. Education and instruction are evolving from transferring the information students must learn or memorize to sorting and analyzing the enormous amounts of information that is already available.
In the past, the only place where information was reliably sorted and analysed was the library. Without question, that is still true. The sorting looks different, the analysis is more complex and libraries have competition from other sources, but the library is the most reliable place to find the information learners need. By extension, librarians, specialists in understanding and using information, have become more important than ever...” (“Overview” in Ideal Libraries: a guide for schools)
IB Mission statement states that The International Baccalaureate aims to develop inquiring, knowledgeable and caring young people who help to create a better and more peaceful world through intercultural understanding and respect.
To this end, the organization works with schools, governments and international organizations to develop challenging programs of international education and rigorous assessment.
These programs encourage students across the world to become active, compassionate and lifelong learners who understand that other people, with their differences, can also be right.
My own summary about how is an IB education different from other systems is that it always emphasizes it is inclusive, meaning respecting for both teachers and learners from different backgrounds, since partly it aims to build a more peaceful world; similar words to “inclusive" are international, global, and boundary breaking, etc. ; It also encourages both teachers and students to consistently improve themselves by giving good approaches to teaching and learning, for myself as a teacher, I have deepened my realization that this world is changing rapidly, I need to keep a young heart to learn and also teach, a life-long learner.
In my own opinion of "inclusive", it can mean cross disciplinary, so comes that I attend lesson planning with other subject teachers, prepare bks into different subjects or even co-teach with other teachers for some activities; it also means comprehensive library resources, therefore to inspire the Ss' sense of agency to learn;
Understanding of IB education makes me more confident about my teaching position that it should be the same as other subject teachers rather than only a "time out" or resource keeping space.
2.2 Library in the IB Documentation & in Our practices
Many IB World Schools have modernized their libraries specifically to challenge perceptions of its function in the community. Despite this, libraries and librarians face problems with how they are perceived, despite the obvious transformation most have made. The phenomenon known as library nostalgia can influence resourcing decisions so that schools even with the best of intentions can underestimate or misunderstand the role libraries and librarians play. (Hochman 2016)
Based on my own working experiences in Dongguan International School, Shanghai American School, Beijing Keystone Academy, and the Affiliated Foreign Language School of SCNU, and also visiting to many schools including Suzhou International Foreign Language School, The Affiliated High School of South China Normal University, Guangdong Country Garden School, I summarized in three aspects:
2.2.1 Librarian's Roles
"Ideal libraries: A guide for schools ", it summarizes the library/ian system with a “6+1” framework, in which librarians are like both an internal hub library governor and also a bridge builder for a wider learning community. Compared with traditional cases, their related roles are accordingly more complex and challenging. It is good that many librarians are making efforts approaching to the ideal description since the big community benefits a lot from these roles. Based on my own experiences and observations, some roles' complementation like co-creator, catalyst or connector are kindly encountering obstacles due to the school's weak educational value or financial support.
2.2.2 Take what the Author Did for an Example
I am currently playing some roles in the "6+1" frame, including managing the library, collecting useful databases for both teachers and students, promoting reading activities, giving library classes, attending collaborative lesson planning. But still I am missing part of the frame either due to my lack of experiences or the weak support, luckily I have the very clear recognition that both me and school should make efforts to get more closely to the standards.
2.2.3 What the Author Saw Other Librarians Do?
The Author saw librarians from Shanghai American school and Keystone Academy give research skill lessons which I think is very excellent since I am currently not giving any to my PYP students yet; they invite authors come to give speech quite often which are very popular with Ss.
The Author saw the very experienced librarians in the affiliated middle school of South China Normal University co work with the library system vendor to invent a new unique library system where people can enjoy more good functions, and this library is voted as the best library space!
Chapter Three Theoretical Framework
Many schools are reconsidering the role of libraries and librarians to make the best of technological and informational resources to enhance learning. Libraries and librarians can drive and support varieties of learning, teaching, and service across the school. Choosing the best approaches to energize the school community is a more complex process, and worthy of ongoing, meaningful conversations that can transform how they impact the community. This resource contains many discussion points and questions which schools can use to inform how their library can be developed. It aims to explore what a library and librarian means for IB schools, and how they integrate into a single system, the library/librarian (library/ian), to enhance learning across the community. The roles that active IB librarians have chosen for themselves are set out and can serve as real-world inspiration for others. This document makes the case that the library/ian can help shape the content, the curriculum and the community in a way that gives learners the best chance to succeed. (Ideal libraries a guide for schools .pdf)
3.1 How is Library Described in IB
The IB definition of a library is designed to focus on maximising its effectiveness: “Libraries” are combinations of people, places, collections and services that aid and extend learning and teaching. The library and the librarian can be thought of as an interdependent system or a library/ian (Tilke 2015). This system consists of active parts which combine to achieve prescribed outcomes, monitor progress towards them, and is efficient and active in its support. This resource refers to both libraries and librarians, but assumes they work together even if there is emphasis on one part of the system over another. (Ideal libraries: A guide for schools)
ATL: Approaches to learning (IB Education)
IB librarians should at a minimum be aware of ATL, ATT and the IB learner profile as they are applied in the programmes offered in the school. They should also be prepared to support both multilingualism and multimodality as outlined in Ideal libraries resources ("The basics of all IB Library/ians” in Ideal libraries: A guide for schools)
As for my school, library always guides Ss rather that ask Ss to get what they want, also encourage them to dig more possible resources that are beyond library. We use agency quite a lot while guiding them to learn, to choose and to comment; In this progress, the Ss' ATL skills develop. Since it is the first year for us to do the PYP exhibition, my own understanding is that library guides Ss to research good resources for referring and teach them how to write correctly.
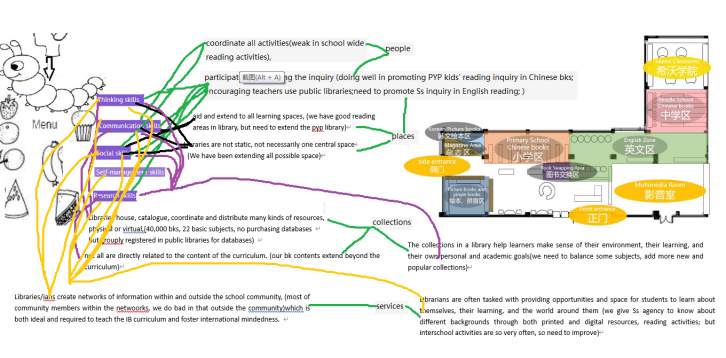
Libraries by their nature generate conversations about life and learning. In the most basic sense, they are repositories of information and stories of the human experience (Lankes 2007) that serve as a basis for inquiry that prompts discussion and reflection. The first conversations need to establish how the library/ian’s role and position is articulated to the community, which sets the conditions for energizing and supporting learning. (Ideal libraries a guide for schools.pdf)
Experienced librarians’ impact and influence on school culture are immediately evident in the collections and services they provide. The language the school uses to describe multiliteracies, inquiry and language development often indicates when a librarian has been integral to school life and culture. In the highest quality IB programmes, librarians are active members of pedagogical leadership teams in the schools or districts they are expected to energize and support.
External circumstances such as budgetary fluctuations, new school construction and the introduction of new technologies impact what is expected of librarians. Many are plunged into uncertainty about their work as schools struggle with resources—a situation which can compromise learning and teaching. External factors such as these can be mitigated to support what a librarian is and can become, and should not obscure what a librarian should do to aid, extend and energize learning and teaching in IB programmes. Even with limited resources, librarians can develop exceptional approaches to energizing IB programmes with the right support and leadership in the school. (Libraries in the 21st century: the struggle between perception and reality)
4.1 Main Conclusions and Findings
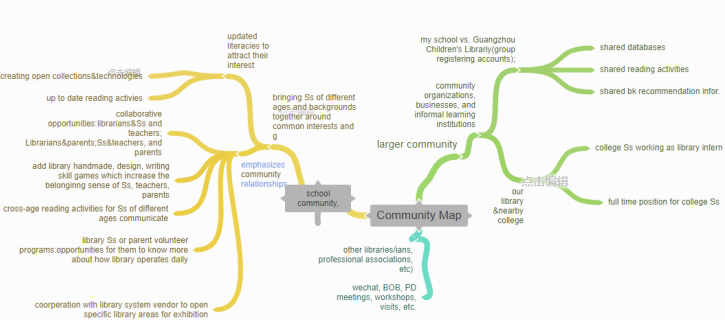
This is the author’s understanding of how to make a library happen under the guid of IB mission:
4.2 Limitations and Implications for Further Study
Though the present study has innovations on the how schools treat libraries, it is limited in terms of its research scope.
First, the present study has confined its subject of study to a certain number of schools either the author has worked in, visited or knowing about, which only form a small part of Chinese schools;
Second, it has focused only on the perspectives of library staff rather than the other staff in schools.
Third, the author of this thesis cannot involve all the aspects of elements which affect a library.
ConnectedLib
Connected Learning: Why connected learning?
IB blog: The librarian’s voice should be heard, as much as any teacher’s
IB blog: Creating a library hub in an IB school
IB blog: Libraries in the 21st century: the struggle between perception and reality
Ideal libraries a guide for schools.pdf